Spis treści:
- What is the metaverse?
- How does the metaverse work?
- Metaverse, VR, AR - how not to get lost in the web of technological terms
- Industry examples - selling in the metaverse
- Controversies surrounding the metaverse - new opportunities, but also new risks
- Does the metaverse have a chance to become the future of eCommerce?
There's no denying that for some time now, we've been living simultaneously in two realities - offline and online - that are increasingly intertwining. A perfect example of this is the eCommerce industry. Online shopping has become incredibly popular, with nearly 80% of Poles using it in 2023 (according to the „E-commerce in Poland 2023" report”). However, the experience of shopping online still differs from browsing products in a physical store. But what if the online and offline worlds not only intertwined but fully merged, offering the benefits of both realities?
This is the vision that the metaverse aims to bring to life, allowing us to enter a 3D virtual reality where you can not only view a product but also feel it. Is this vision merely a dream of tech enthusiasts, or is it truly the direction in which eCommerce is headed? Find out more in this article!
What is the metaverse?
It's difficult to provide a clear and simple definition of the metaverse—after all, it's a concept that is rapidly evolving and taking on various forms. The term gained popularity thanks to video games like Fortnite and Roblox, which allow users not only to play together but also to fully immerse themselves in an alternative reality. Soon, other industries began to tap into the metaverse as well—social media, prestigious brands, and, of course, the eCommerce sector. But how can we most simply explain what the metaverse is?
Put simply, the metaverse can be seen as the next stage in the evolution of the internet, one that brings all its capabilities into a three-dimensional space. In other words, the metaverse is a virtual universe where people exist as avatars. This virtual reality typically consists of many distinct spaces through which all users can move freely. As a result, avatars, much like people in the real world, can perform everyday activities such as going to work, meeting friends, or shopping.
Depending on perspective, the metaverse can be viewed as an alternative to the real world or as a replica, reflecting all the essential aspects of civilization, such as social interactions, currency, trade, economy, and ownership.
How does the metaverse work?
Just like with its definition, the concept of how the metaverse works is hard to pin down within strict boundaries. Creating virtual spaces is a complex process that requires the integration of many advanced technologies. The key ones include:
- VR (Virtual Reality),
- AR (Augmented Reality),
- Blockchain,
- Artificial Intelligence,
- Internet of Things (IoT),
- 3D reconstruction.
It's also worth noting that the biggest players in this market, such as Meta (the owner of Facebook), Microsoft, and Roblox (the creator of one of the most popular online games based on VR), are developing their own metaverse platforms, utilising their unique know-how and technologies. All of this aims to create a new space where people can not only communicate but also work, play, learn, and trade in a completely new and unprecedented way.
In the context of eCommerce, the metaverse is transforming how brands can communicate with customers, offering them more interactive and engaging shopping experiences.
Metaverse, VR, AR - how not to get lost in the web of technological terms
The advancement of technology introduces many new terms that can be confusing, especially when they are used interchangeably. Such conceptual chaos can make it difficult to understand new trends in the industry. Therefore, it’s important to know the differences between various technologies to consciously follow industry trends. Let's focus on three terms that are often confused: AR, VR, and the metaverse - what sets them apart?
The metaverse is a virtual world that often uses VR (virtual reality) and AR (augmented reality) technologies to create an immersive experience. With VR devices, such as glasses or headsets, users can fully immerse themselves in a three-dimensional world, experiencing it not only visually but also audibly - for example, hearing the rustle of leaves moved by the wind. VR allows for complete entry into a virtual space where every element of the world can be interactive and realistic.
AR, on the other hand, overlays digital elements onto the real world, allowing interaction with virtual objects that we see, for instance, through a smartphone screen. It’s a subtler, yet powerful tool that enables users to bring virtual elements into the real world.
Since VR and AR technologies are not yet widely accessible - mainly due to cost - not every internet user can afford to purchase modern goggles or other devices. Therefore, to make the concept of the metaverse more approachable, it can also be accessed through a computer or smartphone screen. However, this experience is less interactive and loses its three-dimensional quality, resembling more of a traditional video game, like the popular The Sims.
Industry examples - selling in the metaverse
"The metaverse provides a much stronger sense of presence," – says Mark Zuckerberg, owner of Facebook, as he promotes this technology. This creates excellent conditions for online stores to build connections with customers. Currently, most companies are utilising only a fraction of the metaverse's potential, collaborating with well-known game creators and setting up single stores or collection exhibits, rather than developing fully-fledged virtual worlds. Brands are also organising virtual events such as fashion shows, product launches, and customer meet-ups.
The metaverse is, therefore, an effective way to stand out in the market and familiarise customers with new technology. Here’s how global brands are incorporating the metaverse into their strategies.
Nike in Fortnite
Nike created the virtual world "Airphoria" in the game Fortnite, offering players a unique brand-related experience. In this alternative reality, players can participate in missions, earn virtual rewards, and explore stylized spaces inspired by sneaker culture.
 Source: https://www.fortnite.com/news/experience-airphoria-in-fortnite-the-ultimate-sneakerhunt?lang=en-US
Source: https://www.fortnite.com/news/experience-airphoria-in-fortnite-the-ultimate-sneakerhunt?lang=en-US
Hyundai in Roblox
Hyundai launched the Hyundai Mobility Adventure project in Roblox, where users can explore a virtual world centred on the future of mobility. This space allows interaction with virtual models of Hyundai cars and technologies, highlighting the brand's commitment to innovation.
 Source: https://www.hyundai.news/eu/articles/press-releases/hyundai-vitalizes-future-mobility-in-roblox-metaverse-space.html
Source: https://www.hyundai.news/eu/articles/press-releases/hyundai-vitalizes-future-mobility-in-roblox-metaverse-space.html
Gucci Garden in Roblox
Gucci created a virtual installation called Gucci Garden in Roblox, allowing users to immerse themselves in the brand’s artistic world. Players can explore themed rooms inspired by Gucci’s campaigns, purchase digital items, and express their style through avatar customization. This project emphasises the brand's creativity and luxurious identity within the metaverse.
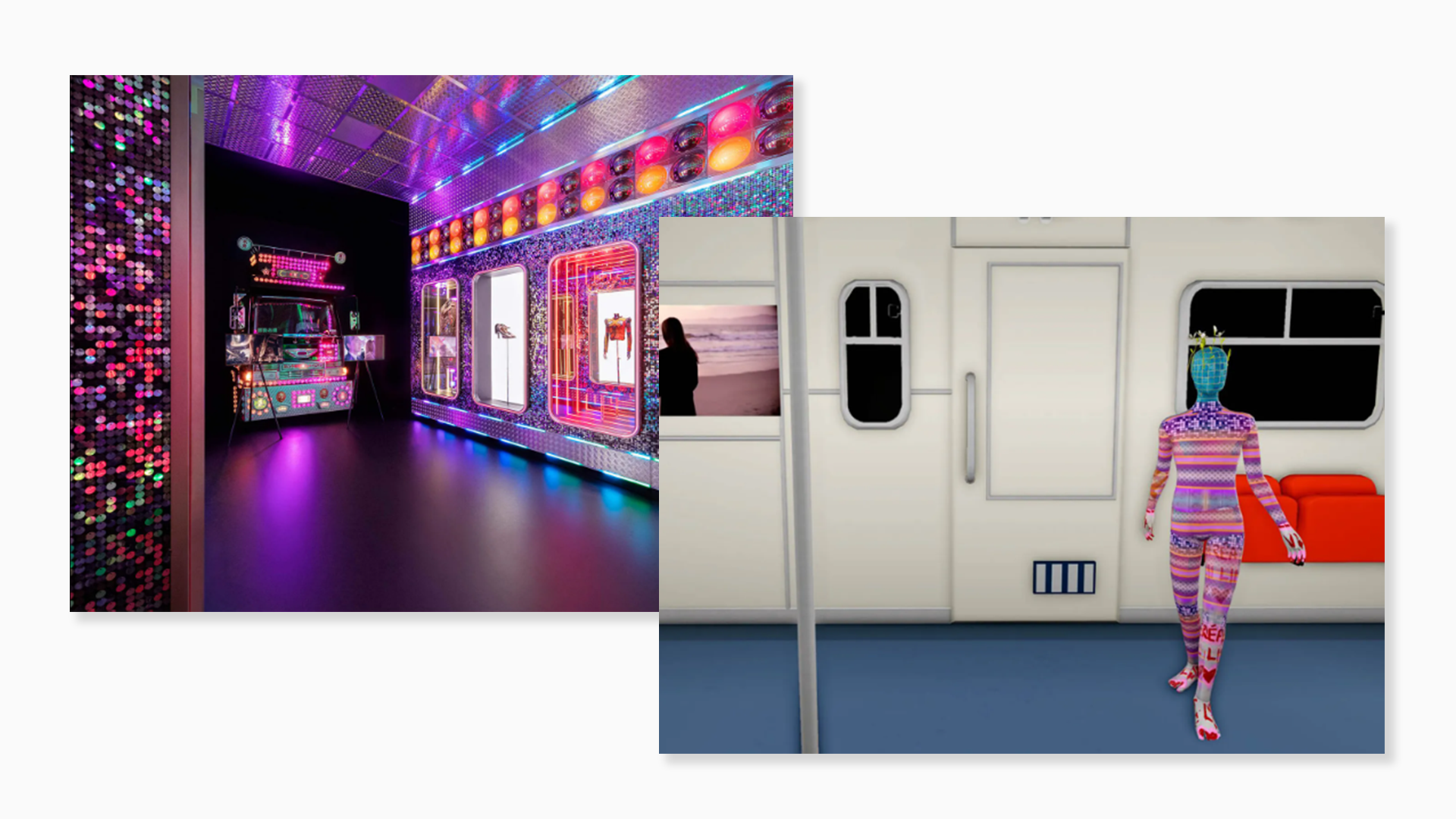 Source: https://www.voguebusiness.com/technology/inside-gucci-and-robloxs-new-virtual-world
Source: https://www.voguebusiness.com/technology/inside-gucci-and-robloxs-new-virtual-world
Controversies surrounding the metaverse - new opportunities, but also new risks
As is often the case with modern technologies, the metaverse evokes both enthusiasm and numerous concerns. Some of these stem from misunderstanding and fear of the new, while others relate to more specific and justified risks associated with the development of this technology. Among these, the following stand out:
Security - one of the main risks associated with the metaverse is cybersecurity. Virtual worlds can become targets for cyberattacks, which could, for example, lead to the theft of personal data. Additionally, many people are concerned that the metaverse, due to the possibility of hiding behind an avatar, may increase user anonymity, which in turn could lead to a rise in antisocial behaviours such as cyberbullying, hate speech, or fraud. This anonymity can make it difficult to identify and prosecute perpetrators, posing a challenge for metaverse creators to implement adequate protection and moderation mechanisms to ensure the space is safe for all users.
Privacy protection - the metaverse collects vast amounts of data, including users' biometric data. There are serious concerns about privacy protection, especially regarding the potential use of this data by companies to monitor and control users.
Environmental Impact - introducing the metaverse on a large scale requires immense computing power. To realise visions such as reading users' emotions and transferring them in real-time to avatars, it may be necessary to increase computing power by up to 100,000 times. This raises questions about the metaverse's impact on the environment and energy consumption.
Availability - currently, VR and AR technology, which is crucial for the full metaverse experience, is expensive and inaccessible to many people. The most popular devices, such as Oculus glasses, cost around $522, while more advanced ones, like Apple Vision glasses, cost over $5220. Additionally, new devices are being developed to fully utilize the metaverse, such as haptic gloves that allow users to feel the weight and texture of virtual objects—further increasing costs.
Usability and convenienc - the devices currently used for VR and AR are often inconvenient. VR glasses are large, heavy, and cumbersome, limiting their use for extended periods. Moreover, the issue of how the brain adapts to switching between virtual and real reality requires further research. How quickly and to what extent our brain learns this switching (and what effects this process has) remains an open question.
Does the metaverse have a chance to become the future of eCommerce?
The metaverse is a fascinating technology that currently allows brands to stand out from the competition—especially those with large promotional budgets. Projects like Gucci Garden or Nike Airphoria demonstrate how virtual worlds can be used to build relationships with younger audiences and create unique experiences. However, despite these innovations, the widespread adoption of the metaverse in eCommerce is still far off.
Firstly, eCommerce customers primarily expect convenience, simplicity, and speed in their shopping experience, which is currently difficult to replicate in the metaverse. Secondly, the technological infrastructure and costs associated with the metaverse limit its accessibility. Until these barriers are overcome, the metaverse will remain merely a curiosity and a tool mainly for premium brands. However, it is worth keeping an eye on the development of this technology because, who knows, it may become a standard in the eCommerce world in the future, revolutionising the way we shop online.