Table of contents:
- Why isn't it working? Identifying the sources of technical issues in eCommerce
- 5 technological pitfalls in eCommerce - common mistakes in online stores
- Avoid technical issues before they impact your business
- eCommerce store without technical problems - the base for online success
Among all online stores that launched a decade ago (in 2014), only 37% remain operational today, according to an analysis by Dun & Bradstreet. Each year, around 8,000 eCommerce businesses shut down. Why does this happen? There are many possible reasons - ranging from poor product quality and ineffective sales and marketing strategies to technology-related issues.
In this article, we'll focus on the technical challenges that eCommerce businesses face. We'll explore the most common technical problems you might encounter when running an online store and provide practical solutions. Keep reading to learn more!
Why isn't it working? Identifying the sources of technical issues in eCommerce
Running an eCommerce business is a dynamic endeavor that requires managing multiple critical areas simultaneously. Beyond sales and customer service, technology management is equally important—and often demands specialized expertise. This is where the first difficulties arise.
Many eCommerce owners lack advanced IT knowledge; their primary focus is on growing the business rather than diving into the intricacies of technology. As a result, technical errors often stem from a lack of awareness about how to effectively manage a sales platform. However, this is just one of the potential sources of issues. Other common culprits include:
- Choosing the wrong IT partner - collaborating with a software house that lacks experience in eCommerce or doesn't understand the nuances of the business often leads to technology misaligned with the company's actual needs.
- Accumulating technical debt - outdated systems, legacy infrastructure, or an unscalable platform - hinders growth and can cause failures during critical periods like peak sales seasons.
- Poorly thought-out integrations with external tools - expanding a store with additional features, such as ERP, CRM, or marketing tool integrations, can lead to technical issues if not planned and executed properly.
- Lack of testing and monitoring - many problems arise from inadequate testing during the implementation of new features or insufficient ongoing platform monitoring.
You can directly influence all of the above issues, minimizing or even eliminating the risk of their occurrence. However, it’s worth remembering that some problems may arise from factors beyond your control, such as unexpected technological changes. The fast pace of technological advancement means that solutions that worked flawlessly a few years ago may no longer be sufficient today. Staying proactive and adaptable is key to overcoming these challenges and ensuring your online store remains competitive in an ever-evolving market.
5 technological pitfalls in eCommerce - common mistakes in online stores
Technical problems can arise at any stage of an online store's operations - from a customer's first interaction with the website, through the purchasing process, to data management and security. While every eCommerce platform is unique, there are common mistakes that frequently appear across the industry. Here are the five most common technical challenges faced by online stores and how to address them.
Slow page load times
In an era of growing customer expectations and lightning-fast deliveries, an online store’s performance must be equally swift. A few years ago, the “3-second rule” applied – that’s how long users were willing to wait for a page to load before leaving. Every second of delay could result in lost potential sales. Today, the situation is even more demanding as every millisecond matters. According to the latest research by Toolster, in 2024, the average time users expect for page loading has dropped to 2.5 seconds.
Slow page loading is often caused by unoptimized images, excessive plugins and scripts, overloaded servers, or lack of caching. With the rise of mobile traffic, poor mobile optimization has also become a significant issue. All these factors burden the website, prolong loading times, and negatively affect user experience (UX).
How to fix this problem?
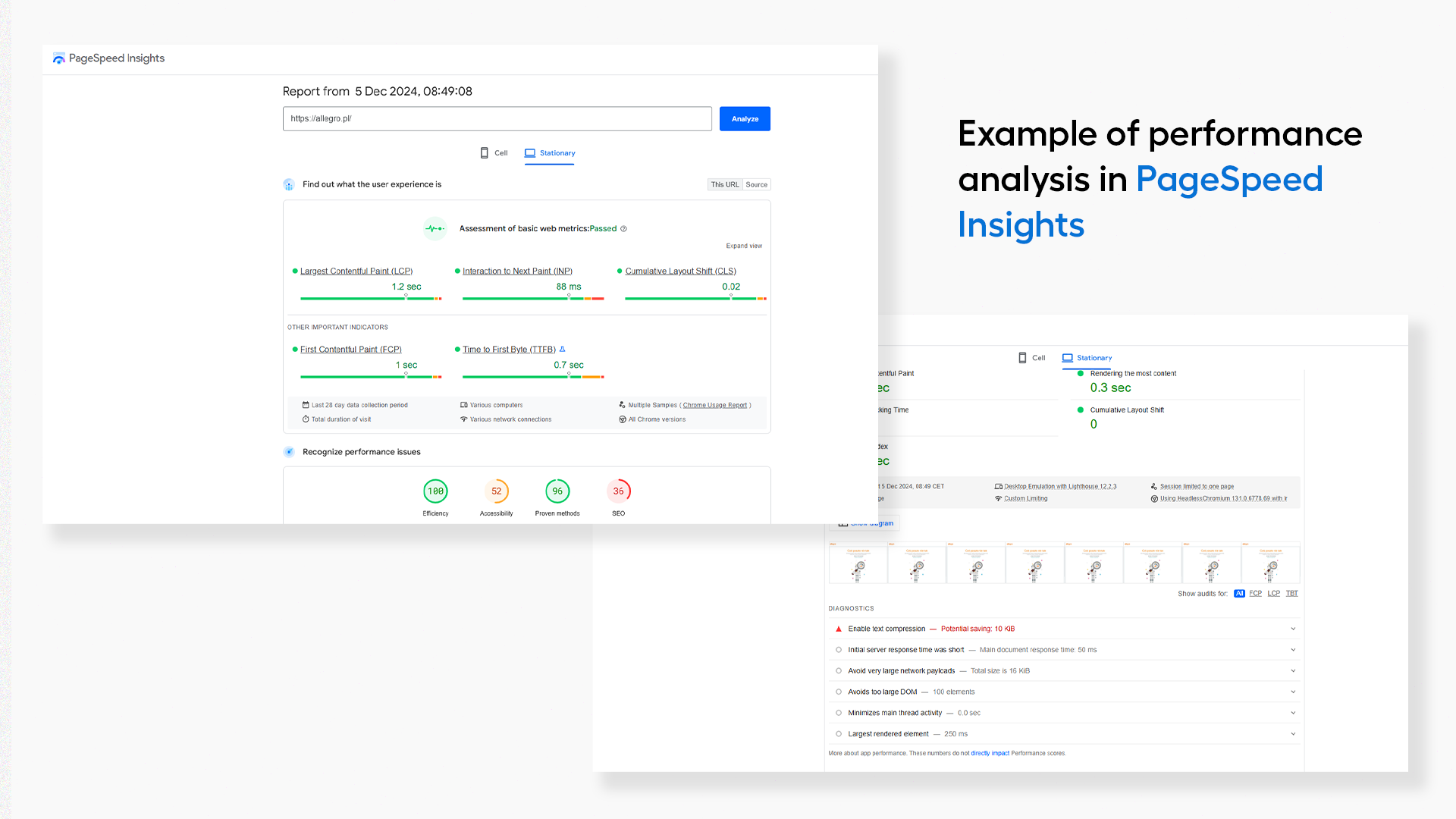
The issue of slow page loading can have multiple causes, and solving it requires a comprehensive approach. Start by analyzing your page speed using tools like Google PageSpeed Insights. These tools can help identify key areas requiring optimization and provide basic recommendations for improvement. For a more in-depth analysis, consider hiring a specialist, such as a software house, to conduct a detailed performance audit of your site. Experts can identify advanced issues such as system architecture errors, inefficient database queries, or problems with external integrations.
Incompatible systems
Online stores rely on various systems to support their operations. Depending on the complexity of their sales processes, these systems can include external tools such as ERP for inventory management, CRM for customer relationship management, PIM for product information management, payment systems, or marketing automation tools. Each system serves a specific purpose, supporting the store's operations and enhancing workflow organization. When implemented correctly, these tools ensure that online sales run smoothly with optimized and well-coordinated processes.
However, for these systems to work harmoniously, proper integration is essential. Problems often arise when the systems are not properly connected, leading to complications such as data synchronization errors - for example, discrepancies in inventory levels between the ERP system and the sales platform. Additionally, inconsistencies in data can cause delays in order fulfillment, while issues with transmitting payment and return information may negatively affect customer service and erode trust in the store.
How to fix this problem?
The solution to these challenges lies in effective system integration. This involves creating a setup that ensures smooth, real-time data exchange between all the tools in use. A key element of such a solution is the use of APIs (Application Programming Interfaces), which are sets of rules and protocols enabling communication between different systems. APIs allow data to flow dynamically and without delays, enabling processes like automatic updates of inventory levels in an online store whenever changes are made in the ERP system.
APIs not only facilitate seamless data exchange but also enable the integration of tools from different providers. This means that systems like payment gateways, CRM, PIM, and ERP can be connected into a cohesive ecosystem, even if they are developed by different companies. Such flexibility ensures the smooth functioning of sales, logistics, and marketing processes while eliminating errors caused by data inconsistencies and improving overall customer service efficiency.
Attachment to monolithic architecture
The opposite of problems caused by poor integration of separate systems is the consolidation of all functions within a single monolithic architecture. While a monolith may initially seem like a convenient and simple solution for an online store, over time, it becomes a significant limitation. All system components - ranging from order management and data storage to payment processing and content management - are tightly interconnected. This means that any change in one module requires modifications to the entire system, which is time-consuming, expensive, and prone to errors.
As the business grows, technological needs become more complex. Adding new features, scaling infrastructure, or quickly responding to changing customer demands becomes essential. In the case of a monolithic system, such changes are difficult to implement because they require intervention in the entire system. Additionally, a failure in one component can impact the operation of the entire store. This can lead to significant financial and reputational losses during critical periods, such as sales events or holiday promotions.
How to fix this problem?
An alternative to the monolithic approach is microservices architecture. By dividing the system into independent modules, each function (e.g., payments, customer service, or product catalog management) operates autonomously. This enables rapid implementation of changes, scalability in specific areas, and reduced risk of failures.
While this approach may be more complex to implement initially, it allows for long-term growth and flexible adaptation of the store to changing market demands. Microservices architecture offers the agility needed to keep up with evolving business and technological requirements, ensuring sustained efficiency and reliability.
Chaos in eCommerce Data
Outdated, incorrect, or inconsistent data is one of the most serious technical problems in eCommerce, with far-reaching consequences for store operations and customer experience. The most common causes of these issues include the lack of a centralized data management system and the manual entry of information, which increases the risk of errors and inconsistencies. Problems can arise in various areas, such as outdated inventory levels and product prices, inconsistent descriptions and images across different sales channels (e.g., marketplaces and eCommerce platforms), or incorrect customer and order data. This "data chaos" not only complicates eCommerce management but also leads to customer frustration, an increase in complaints, and, in extreme cases, a loss of customer trust.
For example, if the inventory system is not synchronized with the sales platform, customers might see products as available when, in reality, they are out of stock. Similarly, incorrect order or customer data can result in delays in shipping, incorrect delivery addresses, or unsuccessful marketing campaigns due to poor targeting.
How to fix this problem?
The solution to this issue is the implementation of systems that centralize data management, such as PIM (Product Information Management) for product data or CRM (Customer Relationship Management) for customer information. These systems ensure that all data is stored in one place and updated automatically across all connected platforms.
In the long term, maintaining high-quality data improves operational efficiency, enhances the customer experience, and supports business growth. By centralizing and automating data processes, businesses can reduce errors, streamline operations, and build lasting trust with their customers.
Neglected eCommerce security issues
eCommerce is one of the most dynamic and rapidly growing sectors of the economy, making it an attractive target for online fraudsters and cybercriminals. The statistics are alarming—in 2023, global costs associated with attacks and financial losses averaged $4.45 million, with the retail and eCommerce sectors accounting for $2.96 million (according to IBM data). This represents more than half of the average global losses, highlighting the scale of the threat to online commerce. Financial losses, however, are just one aspect of the problem. Every security incident is also a blow to a brand's reputation and customer trust. In an era where customer loyalty heavily depends on the sense of security during online shopping, breaching that trust can have long-term consequences.

The most common threats include DDoS attacks (Distributed Denial of Service), which disrupt website functionality; phishing, which aims to steal customer login data; and malware, which can encrypt or steal sensitive information. These threats often arise due to vulnerabilities in security measures, such as the lack of regular system and plugin updates, the use of outdated software, or the failure to implement basic security standards like an SSL certificate.
How to fix this problem?
To effectively protect your business, it’s essential to implement comprehensive security solutions. The basics include regularly updating systems, using SSL certificates to encrypt data transmitted between customers and the store, and ensuring protection against DDoS attacks. Investing in intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDS/IPS) and implementing two-factor authentication for admin panel access is equally important. Additionally, conducting regular security audits and training employees to recognize phishing attempts are essential for maintaining a high level of protection.
Avoid technical issues before they impact your business
Technical Issues Can Lead to Customer Loss, Decline in Sales, and Serious Reputational Damage. It’s far better to prevent these problems than to scramble for solutions once they start affecting your store’s operations. A proactive approach and investment in the right technologies can help you avoid many difficulties, improve the efficiency of your eCommerce operations, and strengthen customer trust. How can you achieve this? Below are key tips to minimize the risk of technical issues:
- Invest in a reliable IT partner – choosing a software house with experience in eCommerce reduces the risk of mismatched solutions.
- Plan for the long term – opt for scalable solutions that will support your business growth for years to come.
- Test and monitor regularly – functional tests and real-time monitoring help identify and fix errors quickly.
- Don’t cut corners on security – system updates, SSL certificates, and protection against DDoS attacks are essential for the smooth operation of any online store.
eCommerce store without technical problems - the base for online success
eCommerce is about more than just selling products - it’s also about leveraging technology to drive growth, enhance customer experiences, and build a competitive edge. If you’re focused on creating a stable foundation for your brand’s online success, we’re here to help.
Reach out to us, and together, we’ll give your online store the technological edge it needs to grow without limits!