Table of contents:
- A Few Words About Magento's Evolution
- Magento 1 vs Magento 2 - key differences
- magento versions – what are the differences?
- Overview of Magento versions
- What’s next? Will Magento 3 be released (and when)?
- Are you maximizing the full potential of Magento in your e-business?
Since its debut in 2008, Magento has become one of the most popular eCommerce platforms. Over the years, it has continuously evolved to meet the needs of modern businesses. Each new version introduces enhanced features, improves security, and boosts performance, but these updates can also require additional time, effort, and budget to implement. What are the key differences between Magento versions? How often should you update the platform, and is every update truly necessary? Finally, could we soon witness a complete revolution with the release of Magento 3? You'll find the answers to these questions in this article.
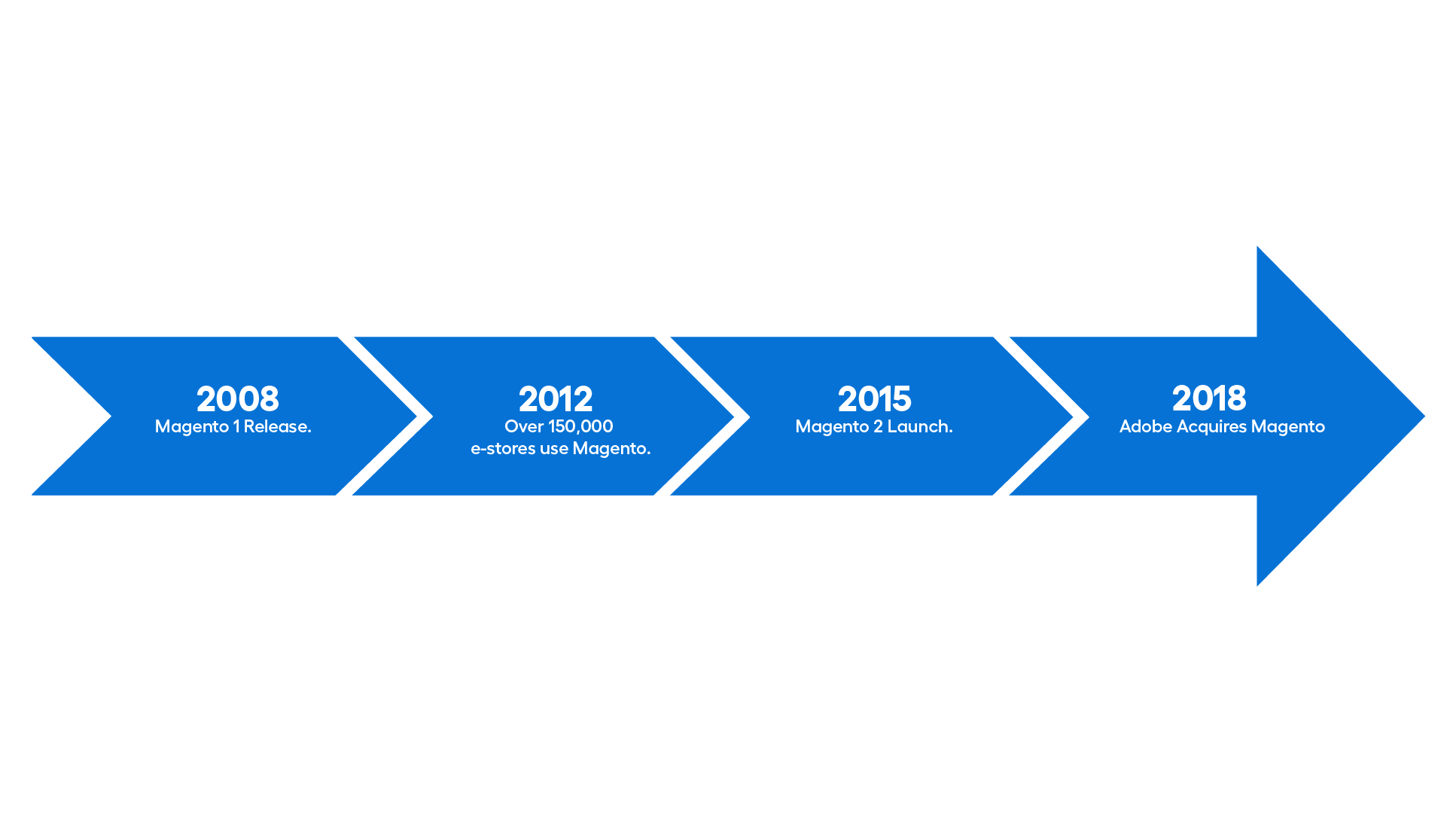
A Few Words About Magento's Evolution
Let’s go back to the early 2000s, when platforms like OpenCart, osCommerce, and Yahoo Stores dominated the nascent internet industry, enabling the creation of some of the first online stores. However, these platforms had their limitations. They lacked flexibility, scalability, and the potential for advanced features.
In response to these challenges, Roy Rubin and Yoav Kutner began working on a project in 2007 that would revolutionize online sales. The result was Magento Community Edition, a free open-source platform launched in 2008. It offered users an unprecedented level of customization. Within a few years, Magento had garnered a massive following, with over 150,000 stores worldwide using the platform by 2012.
The rapid growth of eCommerce brought more sophisticated market demands, and Magento had to adapt. In 2015, the creators released the groundbreaking Magento 2 update. This new version came with a host of improvements, including better performance, enhanced mobile support, improved resource management, and a more user-friendly interface. While this was a major milestone, it also posed challenges for users, as migrating from Magento 1 was a time-consuming yet necessary process - especially with the discontinuation of Magento 1's technical support in 2020.
Another pivotal moment in Magento's history came in 2018 when Adobe acquired the platform. As a result, the platform was rebranded as Adobe Commerce, while the former Magento Enterprise became known as Magento Open Source.
Despite the passage of time and numerous changes, Magento remains one of the most influential tools in the eCommerce world. Its ability to adapt and respond to market needs continues to make it a go-to choice for both small businesses and global corporations seeking flexibility and scalability in running their online operations.
Magento 1 vs Magento 2 - key differences
For many years, Magento 1 dominated the market as a reliable tool for eCommerce. However, as technology advanced, its limitations became increasingly apparent. Despite its strengths, Magento 1 struggled to keep up, particularly with slower page loading times, limited performance, and the growing complexity of store management.
Magento 2 was designed to address these challenges, introducing support for a range of modern technologies such as Symfony, Composer, RequireJS, Knockout.js, and Varnish. What does this mean in practice?
- improved performance and speed - thanks to an advanced caching system and optimized code, Magento 2 offers faster page loading times. The platform can handle higher traffic and more orders, making it a key advantage for growing stores that must meet increasing user demands.
- enhanced admin panel - the Magento 2 dashboard is more intuitive and user-friendly, making it easier to manage products, analyze sales data, and configure settings. This streamlines daily operations significantly.
- integrations and extensions - with its modular architecture, Magento 2 minimizes conflicts between extensions and simplifies the installation of new features. This allows users to customize the platform more easily and efficiently to meet their needs.
- security enhancements - Magento 2 provides regular security updates to protect customer data from potential threats. This is especially crucial in today’s environment, where cybersecurity plays a key role in building trust.
It’s worth noting that practically no one uses Magento 1 anymore, as technical support for the platform ended in 2020. Without security updates or support for modern technologies, using Magento 1 poses significant risks for businesses, especially concerning data protection and regulatory compliance. Magento 1 is now primarily used by companies that have delayed migrating to the newer version or have such complex eCommerce systems that migration requires extensive planning and time. In these cases, migration often involves not only transferring data but also adapting advanced integrations, functionalities, and technical infrastructure.
Magento versions – what are the differences?
The division between Magento 1 and Magento 2 marks key milestones in the platform’s development. The transition from the first version to the second was not a simple update but required a full migration, including databases, functionalities, and external integrations. However, in both cases, the platform’s creators have provided (or continue to provide) regular updates and improvements. Magento versions can be categorized as follows:
- functional updates (introducing new features) - a change in the second digit of the version number (e.g., from Magento 2.3 to Magento 2.4) signals significant upgrades and new functionalities. For example, Magento 2.3 introduced support for PWA Studio, enabling the creation of modern web applications. These updates often require extensive changes, adjustments to external integrations, and thorough testing of new features in the existing environment.
- technical fixes (stability and optimization) - a change in the third digit of the version number (e.g., from 2.4.1 to 2.4.2) involves minor improvements and fixes for identified bugs. These updates enhance system stability, improve existing functionalities, and address user-reported issues. While less invasive, they are equally important for ensuring smooth store operations.
- security fixes (Security Patches) - security updates are marked with the suffix "-p" (e.g., 2.4.5-p1) and focus exclusively on addressing security vulnerabilities. These patches eliminate risks of attacks and protect user and customer data from threats. Regular application of security patches is critical for maintaining a safe store environment.
It’s also important to remember that each Magento version—whether major or minor—has a lifecycle and eventually loses official support. For instance, Magento 1.9 lost support in June 2020, and Magento 2.3 stopped being supported in September 2022. Lack of support means no security updates or new features, exposing stores to vulnerabilities and compatibility issues with modern technologies.
Overview of Magento versions
The latest version of Magento, available as of January 2025, is Magento 2.4.7, released on April 8, 2024. This version focuses on strengthening security, addressing known vulnerabilities, and introducing enhancements to protect both user and customer data. Additionally, Magento 2.4.7 offers support for new payment and shipping methods and includes significant technological improvements (e.g., GraphQL optimization), resulting in faster and more efficient integrations.
The updates in the latest Magento 2.4 version highlight the platform's continuous evolution, delivering functionalities that meet the real needs of modern businesses. Magento consistently provides tools that not only address current challenges but also enable better use of future technological opportunities. Let’s take a closer look at how the various Magento versions over the years have shaped today’s eCommerce landscape.
| Magento Version | Key Updates |
|---|---|
| Magento 1.8 | Improved tax calculation processes, new features, and performance optimizations. |
| Magento 1.9 | Added support for Responsive Web Design, cross-border commerce features, and enhancements to the checkout process. |
| Magento 2.0 | A comprehensive transformation of the platform focused on improved speed, enhanced security, and a more intuitive user experience. |
| Magento 2.1 | Introduced Content Staging and Preview, support for Elasticsearch in Commerce editions, improved PayPal payment methods, and a more user-friendly admin interface. |
| Magento 2.2 | Added advanced reporting, Instant Checkout, Magento Shipping, and new features tailored to the B2B sector. |
| Magento 2.3 | Introduced Progressive Web Apps (PWA) support, Multi-Source Inventory (MSI), improved Elasticsearch, and the Page Builder tool. |
| Magento 2.4 | Strengthened security with Two-Factor Authentication (2FA), improved the media gallery, and further developed Progressive Web Apps. |
What’s next? Will Magento 3 be released (and when)?
Magento 2 was launched around seven years after the debut of Magento 1, which might suggest that the time for another major update - Magento 3 - is approaching. However, there are currently no official announcements from Adobe regarding plans for a new version. The current development strategy indicates that, rather than introducing a completely new version, Adobe prefers to refine the existing platform. This approach allows businesses to benefit from modern tools without the need for costly migrations. As such, the question of Magento 3 remains speculative for now.
Are you maximizing the full potential of Magento in your e-business?
Keeping Magento up to date is crucial for maintaining competitiveness and security in the ever-evolving eCommerce landscape. Using the latest version ensures access to cutting-edge technologies, features, and security measures essential for running a modern online store effectively. Make sure your business is operating on the current version of the platform to leverage its full potential and meet growing customer expectations.
If you need assistance (such as migrating from Magento 2.3 to version 2.4), don’t hesitate to reach out to us!




